You can create a shortcut for programs, folders, and documents that the user regularly accesses. Label is a reference to an object, a means quick access to an object located in a folder on the computer disk or on the network to which the computer is connected. Usually the shortcut is located on the desktop, but it can be placed in any folder as well. Double-clicking a shortcut icon allows you to open a document or run a program regardless of where they are located — on the user's computer hard drive, on a network drive, or on a Web site.
By default, a shortcut has the same name as the object it points to. The shortcut icon, as a rule, differs from the icon of the object for which it was created, only by the transition arrow located in the lower left corner of the picture (Fig. 4.31). The shortcut file has the extension .lnk and takes up little disk space (about 1 KB). It is a special communication file. When you double-click a shortcut, Windows uses the information stored in the link file to find and open the object associated with that shortcut (Figure 4.32).
Rice. 4.31. Shortcut to open Word document
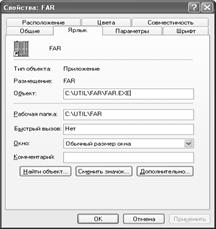
Rice. 4.32. General shortcut properties
To facilitate access to an object: a program or a document, you can create one or more shortcuts and place them in different places: on the desktop and in frequently used folders. For example, if a Word document contains help information that the user is constantly looking at, then by placing its shortcut on the desktop, he will be able to open the file without accessing the menu.
Label can be placed inside a document or message Email... By dragging the file icon onto the shortcut to floppy disk, you can copy the file to a floppy disk. Placing a shortcut to the printer on the desktop allows you to speed up the printing process and make it easier to control it. When you delete a shortcut, the file with which it is associated is not deleted. If you rename a folder / file, the name of the shortcut will not change, but the link between them will remain.
You can create a shortcut to a disc, program, folder, or document using one of the methods below.
1. Select the object for which the shortcut is created in the window My computer or conductor and select from the menu File command Create shortcut A new shortcut will appear in the lower corner of the folder window where the object is located. Then you need to drag the shortcut with the mouse to Right place such as the desktop.
2. Select the object for which the shortcut is created in the window My computer or conductor, then activate the command Copy on the menu Edit... After going to the window of the folder in which the shortcut is supposed to be placed, select the command Insert shortcut on the menu Edit.
To delete a shortcut, select it, press the Delete key, or right-click the shortcut and select the command Delete... In both cases, Windows will ask you to confirm the specified action to avoid accidentally deleting the object.
Creation of documents.
Create folders.
OPERATIONS WITH OBJECTS.
List of the most important operations with objects:
Creation of new objects: folders, documents, shortcuts;
Selection of objects: one, two and all at once;
Copying and moving objects using the command menu, mouse and clipboard;
Renaming objects;
Removing objects;
Object restoration;
Search for files and folders;
Launching programs.
1. Select the place where you want to create the folder: on the Desktop, disk or in some folder.
2. Open the corresponding window.
3. Right-click on free space window. A context menu appears.
4. Select the Create item in the context menu and execute the folder command.
5. In the label field of the icon, enter the name of the folder
1. Open the folder where you want to create a new document.
2. Right-click on an empty space inside the folder. A context menu appears.
3. Select the Create item in the context menu, select the type of the required document and left-click on it.
4. In the label field of the document icon, enter the desired name.
Labels are created in much the same way as folders and documents. But there is one peculiarity when creating shortcuts. If a name was entered for folders and documents, then for the shortcut you need to specify the object to which it refers, after which Windows 95 will itself suggest a name for the shortcut, if desired, you can change it. Labels can be created in two ways.
To create shortcuts using the first method, you need:
1. Open the folder in which you want to create a shortcut.
2. Click the right mouse button on the free space of the folder. A context menu appears.
3. Select the Create item in the context menu and execute the Shortcut command.
The Create Shortcut window opens to help you find the desired object and the folder in which it is located. Click the Browse button, find the desired folder, click on it 2 times, the folder opens, find desired file, click on it 2 times, the command line is formed. Click Next, the name of the shortcut appears, you can change it if necessary, click Next, a set of shortcuts is proposed, select the desired one, click on it,
To create shortcuts using the drag and drop method:
1. Open on the screen two folders - the folder in which the original object is located and the one in which the shortcut of this object will be placed.
2. Pressing the right mouse button drag an object from one folder to another.
3. In the context menu. Which will appear after completing this operation, click on the Create shortcut command. Windows 95 sets the shortcut icon and title automatically. You can change them if you want.
It is convenient to create shortcuts for calling frequently used programs.
How is a shortcut different from simple files and folders, what is a shortcut? To answer these questions, first let's remember what we do when we need to open some program (folder or file). We look for the icon for this element and click on it. For example, to open the "trash" folder, we click on the corresponding icon: Have you noticed that some icons have an arrow in the lower left corner?
These arrow icons are called shortcuts. The external difference is clear, but what is the main difference?
A shortcut is a file that refers to the address where a program, folder, or other document is actually located.
Let us explain with the example of a typical life situation: we go to the store and suddenly there is a note on the door: “ we have moved, now drive through the whole city to our new address! ". An unpleasant situation, but at least we know that the store has not closed.
The shortcut is the same note to the computer: “ the original file is not here, but it sits in a different place, look there! " That is, the file has not gone anywhere, has not escaped from the computer, but is located in a different location. And unlike the situation with the store, you don't need to go far, the computer instantly finds the right address and opens the file.
Why create desktop shortcuts
1. To quickly launch programs.
It is a very flexible and convenient tool: this window always appears first, you do not need to search for it, it is enough to minimize all windows and we already see a background image with icons and. For convenience, the documents that are used most often are stored on the desktop, because they can be launched immediately after turning on the computer, without opening other folders. It is much faster to launch it by clicking on the corresponding icon on the desktop than to search for the program in the start menu.
2. For cleanliness and order.
Often we save all new files to the desktop at once to find them quickly. But the more documents, the more difficult it is to find what you need and not get confused. If you install programs and save all the pictures to your desktop, then soon it will be cluttered:
It is much more efficient to leave only those icons and shortcuts on the table that you really use often. And let the rest lie in the folders in their places.
3. To save space on system disk.
But the most important reason is different: the desktop is not just a picture on which icons of programs and files lie. By its functions, the desktop is the same folder as the rest, that is, it stores different documents, with the only difference that it is displayed differently: it is always visible and attracts attention. We can say that the main table folder is the Queen of all folders! But nevertheless, it retains all the properties of the usual, that is, it can be found and opened on the hard disk. It is easy to verify this, just open it:
- go to My computer,
- open drive C :,
- find the folder "Users" or "users" inside,
- there select the folder with the name that you named the computer
- find "desktop" or "Desktop" inside this folder
Are you convinced?
And what did this knowledge give us? The fact that the files and programs that we see on the desktop actually lie inside this folder and take up space. And the desktop folder itself is in the system drive, that is, the volume on which it is installed (usually, this is drive C). And on, if possible, it is better to keep them on another hard drive, and for quick access to do just shortcuts on the desktop, which weigh very little.
What shortcuts can you create
Shortcuts can be anything: you can make a shortcut to any text document, folders, any program, movie and even a website. We will talk about the latter in more detail below.
So, we figured out what a shortcut is and why you need to create it, now let's move on to practice.
Create shortcut
The two most simple ways creating a shortcut: using the mouse and using the mouse and keyboard. The Simple & Simple team recommends using the keyboard method because it is faster.
How to create a desktop shortcut using the keyboard
How to create a desktop shortcut using a mouse
Practical task:
- Find the desktop folder on your computer
- Create a shortcut to your desktop folder
- Put your desktop shortcut on your desktop!
-
File format:
File size:
Type of work:
Not selected
Informatics, VT, telecommunications
Assigning shortcuts. Ways to create shortcuts. Configuring the parameters of shortcuts and modes of their operation for p ...
You can find out the cost of helping to write a student paper.
Help in writing a work that will definitely be accepted!
Label is a small file that links to another file or folder. As a file, a shortcut has a name and an icon. The main locations for shortcuts are the Windows Desktop and Main Menu. Yes, in fact the Main Menu mainly contains shortcuts and folders. But it can also contain regular files. Shortcuts and files are drawn as menu items, while folders are drawn as submenus. You can verify this by examining the "Main Menu" folder in the "Windows" folder. Next to it is the "Desktop" folder. It is the contents of this Windows folders draws us at startup on the monitor screen. That is, "Main Menu" and "Desktop" are two special folders in Windows.
The main purpose of shortcuts- provide quick and convenient access to files and folders located in the depths file system hard drive.
It's easy to create a shortcut. There are special commands for this in the Explorer window menu. On the File menu, there is a New Shortcut command. This command creates a shortcut in the same folder as the file it points to. Then it can be copied to other folders, including the Desktop and the Main Menu. But there is an even more convenient command. In the same place in the "File" menu there is a submenu "Send". In the "Send" submenu we will find the item "Desktop (create shortcut)".
Windows can create a shortcut to the file or folder on which the cursor is located, and immediately place this shortcut on the Desktop. Both commands for creating shortcuts are also present in the context menu.
Create a shortcut by dragging and dropping files- most quick way bringing a shortcut to the desktop is "drag and drop", that is, select the required file and then simply drag it to the desktop. When dragging, a shortcut icon must appear on the icon, if for some reason it does not appear, then the file or folder is either transferred or copied (when dragging the + sign on the icon).
Create a shortcut using context menu
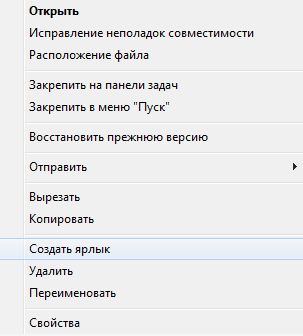
... Let's create a shortcut for the Calculator program. To do this, you need to right-click on the desktop. A menu will appear on the screen where you need to select the "Create" item.
A new menu appears: in this menu it is necessary to select the item " Label"
Then a window appears " Creation shortcut". In the window that appears, click on the" Overview",
and then double click on the small folder Windows. The window that opens contains all the programs in the folder Windows... To see the program " Calculator", you need to scroll the scrollbars. Having found the program " Calculator", you must double-click on the icon Calculator", which is to the left of the program name.
After that, in the command line of the window " Creation shortcut"the path and name of the selected program appears
Now a shortcut for the calculator program will appear on the desktop, which can be dragged to any convenient place.
Another way to create a shortcut is to select a file or folder and right-click, then select a position " Create label", you can also do this by selecting" File \ New label".
When you perform this action, a shortcut will appear in the root of the folder in which the above action was performed. Now this shortcut can be copied or moved to the desktop, or to another place we need.
Change parameters shortcuts and them deletion... To change the parameters of a shortcut, for example, the type of window that opens, you need to right-click the shortcut and select the command " Properties".
To remove a shortcut, you need to drag it to the " Basket"or press the button" Delete". Removing the shortcut does not affect the object itself.
During the transition fromDOSToWindows the user interface is simplified, often eliminating the need for not only the command line, but also batch files. Although this is justified by the potential inherent in Windows, it still significantly impoverishes the possibilities for managing a PC.
In DOS, a shortcut to an MS-DOS program is a Pif file, which is also a system configuration program. An inexperienced user is often afraid to resort to command lines, because he doubts the correctness of the commands entered and fears to spoil something. In addition, incorrect commands are inconvenient to edit - you have to retype them, unless, of course, there is a Doskey utility. In general, simple commands are easy to learn to quickly enter directly, but when it is necessary to execute a whole series of them, in particular to archive, rename, move or copy groups of files, and also if such operations are required often, then it makes sense to refer to the Bat file. It is best to use a simple file name so that no errors occur when you type it. The Windows system allows you to make file operations more intuitive, and to give an expressive shortcut to the faceless DOS Bata files.
If, for example, there are more than 50 computers in the network and all users, as a rule, are well aware of their programs and standard operations in NC and Windows, then in order to change the properties of a shortcut to one of the public programs and add two subfolders to each of the PC can do the following. Place a shortcut "Shortcut.lnc" with the necessary properties in a public folder, batch file"Command.bat" and a shortcut "Command.pif" to it with an icon, for example, in the form of an airplane (Windows \ System \ Pifmgr.dll). The Bat file included the following lines:
DEL C: \ WINDOWS \ WORKING ~ 1 \ LABEL.LNC
COPY F: \<ПУТЬ>\ LABEL.LNC
C: \ WINDOWS \ WORKING ~ 1 \ LABEL.LNC
In the shortcut properties for this file, you must also include the "Close window when session ends" feature. Now the procedure for replacing the shortcut and creating two subfolders on each of the 50 machines is just to click on the icon with the image of an airplane in the window of a shared network folder.
It happens that similar tasks need to be solved for a local PC. For example, before working on a document, you should unzip the files on the floppy disk, and then zip them again after finishing. In addition, it is necessary to organize the files in a certain way, placing them in different folders. In this case, the set of commands depends on the archivers used.
Many programs are command-line controllable. Moreover, this turns out to be more flexible than the usual mouse click on its b
icon. In such a case, batch files and shortcuts will help. In properties Windows shortcuts(Lnc files) there is also a place for the command line, which points to the batch file that is launched along with the corresponding shortcut.
Windows Explorer (explorer.exe) can be launched with the parameters specified in the properties of its shortcut or in a batch file:
/ n - open the explorer in a single window with the contents of the current folder;
/ e - open the explorer with the contents of the current disk and the expanded current folder;
/ root,<имя>- specify the folder, the contents of which you want to view.
Command c: \ windows \ explorer. exe / e, / select, c: \ dir1 \ file.doc will open explorer with the expanded directory DIR1, and c: \ windows \ explorer.exe / n, / root, c: \ dir1 \ file.doc will call text editor(in this case - Word) and will open the document, and if Word is not installed, then an error message will appear.
Commands will be executed the same way from the command line (DOS session) and from the corresponding shortcut. However, to avoid problems due to incorrect encoding, the names of directories and files should be entered in Latin letters. So, the previous command is not implemented if the path contains the names of folders in Russian in Windows encoding.
Sometimes you need to run a program in Windows that can only work in the DOS environment. In this case, the batch files will again help. For example, you can play GTA on both Windows and DOS, but when the system is overloaded with programs executing at a particular point in time, GTA "will not work" and you will have to use the DOS emulation mode. To speed up this process, you need to perform certain operations. First, create and place a shortcut to the DOS session on the Desktop. Then, by opening the properties of the shortcut, add the name of the batch file that will control the launch of the program, and create this file, for example, under the name Igra.bat.
Then, being in the "Program" tab, you must click the "Advanced" button, enable the options "Prevent the program from detecting Windows", "MS-DOS mode", "Select a new MS-DOS configuration" and fill in the fields for files.
Closing additional settings program, you can change the icon for it by selecting it using the "Browse" button from those already in the system. So, to run the program, just click on the shortcut. At the end of the work, you need to type Exit in the command line and press
In some cases, you can reboot the system using a batch file. So, for DOS mode there is a utility called Restart, the executable file of which (restart.com) is located in the c: \ windows \ command \ ebd \ ebd.cab directory. For Windows dll, SHExitWindowsEx 8 - also turn off the PC (if this function is available).
similar Bat files. For example, AVP with default settings and running AVP monitor will not even allow copying such a file. However, certain settings will help to cope with this problem as well.
For command file options in Windows, you can display a dialog box. So, let's create a file Mydel.bat to delete the file we specified in the future.
IF exist% 1 Del% 1
On the command line, after the name of the batch file, the name of the file to be deleted is indicated.
Let's create a shortcut to the Bat-file and in its properties on the “Program” tab and in the “ Command line"Add a question mark at the end of the line, separated by a space. We will enable the function "Close the window at the end of the session" and so change the icon to match the nature of the command. As a result, after double-clicking on the shortcut of this file, the "Options" window will appear, where you must enter the full name of the file that we are going to delete. To complete this command, you just need to indicate OK. Here it should be borne in mind that a file deleted in this way will not be placed in the Trash and, of course, it will also not be possible to return it.
Finally, let's create another batch file Ar.bat that allows us to perform several functions at once:
· Checking a floppy disk for files and deleting them;
· Archiving and sending to a floppy disk together with pictures in .JPG format of the article just written, for example Bat.doc, which will be located in the% 1 subdirectory of the Maydoc1 directory (enter the name of the subdirectory in the parameters window). Files with other extensions will remain unchanged in the working directory;
· Shutdown of the computer.
Having opened the properties of the Bat-file or its shortcut, enter the question mark at the end of the command line, separated by a space. In the root directory of the C: \ drive, create a service file, which may come in handy more than once in the future. It will be a text file named Y, without an extension, containing only one Y character. In the first line of the Bat file, the Y character gives an affirmative answer to the Del command's request to delete files. Place the Ar.bat file itself in the root directory of the C: \ drive and, opening the shortcut properties, specify C: \ in the “ Work folder»Of the" Program "tab. Select the icon for the shortcut from the catalog
Windows \ System \ Shell32.dll. Drag the shortcut to the Desktop, insert a floppy disk with old and unnecessary files into the floppy drive and, after saving the document, close Word and click on the AR shortcut.
A shortcut is a small file that links to another file or folder. As a file, a shortcut has a name and an icon. The main locations for shortcuts are the Windows Desktop and Main Menu. Yes, in fact, the Main Menu basically contains shortcuts and folders. But it can also contain regular files. Shortcuts and files are drawn as menu items, and folders are drawn in the view submenu. You can verify this by examining the "Main Menu" folder in the "Windows" folder. Next to it is the "Desktop" folder. It is the contents of this folder that Windows draws to us at startup on the monitor screen. That is, "Main Menu" and "Desktop" are two special folders in Windows.
The main purpose of shortcuts is to provide quick and convenient access to files and folders located in the depths of the hard drive file system.
It is very easy to create a shortcut; there are special commands for this in the Explorer window menu. In the File menu there is a New Shortcut command. This command creates a shortcut in the same folder as the file it points to. Then it can be copied to other folders, including the Desktop and the Main Menu. But there is an even more convenient command. In the same place, in the "File" menu, there is a submenu "Send". In the submenu "Send" we will find the item "Desktop (create shortcut)".
Windows can create a shortcut to the file or folder on which the cursor is located, and immediately place this shortcut on the Desktop. Both commands for creating shortcuts are also present in the context menu.
Create a shortcut by dragging and dropping files — The fastest way to bring a shortcut to the desktop is to drag and drop — that is, select the file you want and then simply drag it to the desktop. When dragging, a shortcut icon must appear on the icon, if for some reason it does not appear, then the file or folder is either transferred or copied (when dragging the + sign on the icon).
Create a shortcut using the context menu. Let's create a shortcut for the Calculator program. To do this, right-click on the desktop. A menu will appear on the screen where you need to select the "Create" item.
A new menu appears: in this menu it is necessary to select the item "Shortcut"
Then the "Create shortcut" window appears. In the window that appears, click on the "Browse" button,
Then double click on the small Windows folder. The window that opens contains all the programs in the Windows folder. In order to see the Calculator program, you need to scroll the scroll bars. When you find the Calculator program, double-click the Calculator icon to the left of the program's name.
After that, the path and name of the selected program appears in the command line of the "Create shortcut" window.
Now a shortcut for the calculator program will appear on the desktop, which can be dragged to any convenient place.
Another way to create a shortcut is to select a file or folder and right-click, then select the "Create Shortcut" option, or you can do this by selecting "FileCreate Shortcut".
When this action is performed, a shortcut will appear in the root of the folder in which the above action was performed. Now this shortcut can be copied or moved to the desktop, or to another place we need.
Changing shortcut parameters and deleting them. To change the parameters of the shortcut, for example, the type of the opened window, you need to right-click the shortcut and select the "Properties" command.
To delete a shortcut, you need to drag it to the "Trash" icon or press the "Delete" key. The object itself is not affected by deleting the shortcut.
Moving from DOS to Windows simplifies the user interface, and often eliminates the need not only for the command line, but also for batch files. Although this is justified by the potential inherent in Windows, it still significantly impoverishes the ability to manage a PC.
In DOS, a shortcut to an MS-DOS program is a Pif file, which is also a system configuration program. An inexperienced user is often afraid to resort to command lines, because he doubts the correctness of the commands entered and fears to spoil something. In addition, incorrect commands are inconvenient to edit - you have to retype them unless, of course, there is a Doskey utility. In general, simple commands are easy to learn to quickly enter directly, but when it is necessary to perform a whole series of them, in particular to archive, rename, move or copy groups of files, and also if such operations are required often, then it makes sense to refer to the Bat file. It is best to use a simple file name so that no errors occur when you type it. Windows system allows you to make operations with files more visual, and impersonal in DOSBat files to give expressive shortcuts.
If, for example, there are more than 50 computers in the network and all users, as a rule, are well aware of their programs and standard operations in NC and Windows, then in order to change the properties of a shortcut to one of the public programs and add two subfolders to each other, you can do the following ... Place the shortcut "Shortcut.lnc" with the necessary properties, the batch file "Command.bat" and the shortcut "Command.pif" to it with an icon, for example, in the form of an airplane (Windows SystemPifmgr.dll), into the public folder. The Bat file included the following lines:
COPYF:<ПУТЬ>LABEL.LNC
C: WINDOWS WORKING ~ 1 LABEL.LNC
The shortcut properties for this file must also include the "Close window on session end" feature. Now the procedure for replacing the shortcut and creating two subfolders for each of the 50 cars is just to click on the icon with the image of an airplane in the window of a shared network folder.
It happens that similar tasks need to be solved for a local PC. For example, before working on a document, you should unzip the files on the floppy disk, and then zip them again after finishing. In addition, it is necessary to organize the files in a certain way, placing them in different folders. In this case, the set of commands depends on the archivers used.
Many programs allow command line control. Moreover, this turns out to be more flexible than the usual mouse click on its b
icon. In such a case, the command files and shortcuts will help. In the properties of Windows shortcuts (Lnc files) there is also a place for the command line, which points to the batch file that is launched together with the corresponding shortcut.
Windows Explorer (explorer.exe) can be launched with the parameters specified in the properties of its shortcut or in a batch file:
/ n - open the explorer in a binary window with the contents of the current folder;
/ e - open the explorer with the contents of the current disk and the expanded current folder;
/ root,<имя>- specify the folder, the contents of which you want to view.
The command c: windowsexplorer.exe / e, /select,c:dir1file.doc will open the explorer with the expanded directory DIR1, and c: windowsexplorer.exe / n, / root, c: dir1file.doc will call a text editor (in this case - Word) and open document, and if Word is not installed, an error message will appear.
Commands will be executed the same way from the command line (DOS session) and from the corresponding shortcut. However, to avoid problems due to incorrect encoding, the names of directories and files should be entered in Latin letters. So, the previous command is not implemented if the path contains the names of folders in Russian encoded by Windows.
Sometimes you need to run a program in Windows that can only run in the DOS environment. In this case, the batch files will again help. For example, you can play GTA on both Windows and DOS, but when the system is overloaded with programs running at a particular point in time, GTA "will not work" and you will have to use the DOS emulation mode. To speed up this process, you need to perform certain operations. First, create and place a shortcut to the DOS session on the Desktop. Then, by opening the properties of the shortcut, add the name of the batch file that will control the launch of the program, and create this file, for example, under the name Igra.bat.
Then, being in the "Program" tab, you must click the "Advanced" button, enable the options "Prevent the program from detecting Windows", "MS-DOS mode", "Select a new MS-DOS configuration" and fill in the fields for files.
Having closed the additional settings of the program, you can change the icon for it by selecting it using the "Browse" button from those already in the system. So, to start the program, just click on the shortcut. At the end of the work, you need to type Exit in the command line and press
In some cases, you can reboot the system using a batch file. So, for DOS-mode there is a utility called Restart, the executable file of which (restart.com) is located in the c: windowscommandebdebd.cab directory. For Windows dll, SHExitWindowsEx8 - also turn off the PC (if this function is available).
It should be noted that some antivirus programs are not "friendly" with
similar Bat files. For example, AVP with default settings and running AVP monitor will not even allow copying such a file. However, certain settings will help to cope with this problem as well.
For command file options in Windows, you can display a dialog box. So, let's create a file Mydel.bat to delete the file we specified in the future.
IFexist% 1
In the command line, after the name of the batch file, the name of the file to be deleted is indicated.
Create a shortcut to the Bat-file and in its properties on the "Program" tab and in the "Command line" field add a question mark at the end of the line separated by a space. We will enable the function "Close the window at the end of the session" and so change the icon to match the nature of the command. As a result, after double-clicking on the shortcut of this file, the "Options" window will appear, where you must enter the full name of the file that we are going to delete. To exit this command, you just need to specify OK. Here it should be borne in mind that a file deleted in this way will not be placed in the Trash and, of course, it will also not be possible to return it.
Finally, let's create one more batch file Ar.bat that allows us to perform several functions at once:
·
checking the floppy disk for files and deleting them;
·
archiving and sending to a floppy disk along with pictures in .JPG format of the article just written, for example Bat.doc, which will be located in the% 1 subdirectory of the Maydoc1 directory (we will enter the name of the subdirectory in the parameters window). Files with other extensions will remain unchanged in the working directory;
·
shutting down the computer.
After opening the properties of the Bat file or its shortcut, enter a question mark at the end of the command line through a space. In the root directory of the C: drive, create a service file, which may come in handy more than once in the future. It will be a text file with names Y, and without an extension, containing only one character Y. In the first line of the Bat file, the character Y gives an affirmative answer to the Del command's request to delete files. The file Ar.bat itself will be placed in the root directory of the C: drive and, having opened the properties of the shortcut, we will indicate C: in the "Working folder" field of the "Program" tab. Select the icon for the shortcut from the directory
WindowsSystemShell32.dll. Drag the shortcut to the Desktop, insert a floppy disk with old and unnecessary files into the floppy drive and, after saving the document, close Word and click on the AR shortcut.
Dnipropetrovsk University of Economics and Law
Kremenchug Institute
Department of Informatics and Mathematical Methods in Economics
Test
from the discipline "informatics"
Topic: “Assigning shortcuts. Ways to create shortcuts. Configuring shortcut settings and modes of their operation for DOS and Windows programs "
Option number 6
Performed:
student of group BZ - 12
Koretskaya M.V.
Checked:
Teacher
Zhigar A.A.
result of checking: